עבודה אקדמית? חפשו עכשיו במאגר הענק, האיכותי והעדכני ביותר:
הנחה 12% על כל מאגר העבודות האקדמיות !!! בעת "חרבות ברזל" : קוד קופון: מלחמה
ב"ה. אנו חב"דניקים ולא נחטא בגזל: יש גם עבודות אקדמיות בחינם (גמ"ח). 15,000 עבודות אקדמיות במחיר שפוי של 99 - 390 שח. סרטון על מאגר העבודות האקדמיות
לא מצאתם עבודה מתאימה במאגר? סמסו לנו דרישות לכתיבה מותאמת אישית - ונפנה למומחה חיצוני בעל תואר שני בתחום שלכם לכתיבה הנתפרת לצרכים שלכם בדיוק!

5% הנחה ב-פייבוקס
עבודות אקדמיות "חמות":
עבודה על החותים התימנים
עבודה בנושא מלחמת חרבות ברזל
עבודה על פסילת חוקי יסוד, בג"צ דיון מורחב, עילת הסבירות
סמינריון על חוק הנבצרות ביבי, בג"צ 2024
עבודה על מחאה נגד הרפורמה המשפטית 2023
רפורמת שר המשפטים יריב לוין, פסקת ההתגברות, ממשלת נתניהו 2023
מחדל הפריות אסותא- החלפת עוברים
בן גביר - ימין פוליטי עולה 2022-2023
מבצע שומר החומות: עזה-רקטות-חמאס 2021
אסון מירון, דוחק הילולת בר יוחאי
הסתערות על הקפיטול, תומכי טראמפ
דובאי 2021: שלום מדינות ערב
עבודת סמינריון על נשים בפוליטיקה
סמינריון בחירות מפלגות אווירה 2021
מצגת אקדמית אלאור אזריה- 99 ש"ח
סרטון הסבר מאגר העבודות האקדמיות
עבודת תזה רפואת שיניים בחינם, באנגלית ENDODONTIC TREATMENT VERSUS IMPLANT D.M.D THESIS (עבודה אקדמית מס. 9919)
0.00 ₪
45 עמודים.
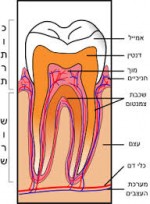
עבודה אקדמית זו בקובץ PDF ולא הכי עדכנית ולכן בחינם. העבודות האקדמיות שברחבי המאגר שבתשלום הן בקובץ וורד פתוח ועדכניות כל זכויות היוצרים שמורות למחבר
Table of Contents
1. Introduction 03
2. History
2.1. History of Endodontics 05
2.2. History of Implantology 10
2.3. Methods in Endodontics and implantology therapy 13
2.3.1. Endodontic Microsurgery to Save Teeth 15
2.3.2. Same day (Immediate) load implantation 17
3. Factors influence the treatment plan
3.1. Survival rates 19
3.2. Patient factors 24
3.3. Treatment duration 27
3.4. Esthetics concerns 29
3.5. Treatment Cost 31
3.6. Risk factors 33
4. Conclusion
5. Acknowledgment
6. References
1. Introduction
Dentists frequently face the predicament of whether to endodontically treat a dubious tooth
or to replace it with an implant. Dentists make the decision for extracting a tooth based on
risk factors such as periodontal and endodontic criteria, remaining tooth structure, size of
previous restorations and the strategic level of a tooth within the dentition. A single
recognizable risk can be easy to manage clinically, but presence of multiple risk factors
endanger the survival of a compromised tooth.[114][156]
Literary data are the foundation for the risk evaluation and long-term prognosis
determination of the tooth requiring root canal treatment (RCT) or extraction and
replacement with an dental implant. The literature, contains contradiction in terms of the
meaning of success and survival of endodontically treated teeth and implants.[70]
Likewise, the reported success rates do not equate to the likelihood of a aid and abet
outcome when applied to a special case.[73]
Iqbal and Kim found that much more rigorous outcome criteria were applied to the
evaluation of ‘successful’ RCT, inclusive the lack of a periapical radiolucency. On the other
hand, the use of less rigorous criteria in dental implantology may interpret to higher rates
of success.[70]
In accordance with a review, the survival of healthful and treated teeth is greater than that
of implants, provided that dental implant loss before loading was added to that during
function over 10 years.[56]
Additional misunderstanding is provoked since, in some studies, retention or survival rates
including successful teeth and also implants classified as surviving. The reader in implant
studies must know the differences in outcome data based on the restoration or implant
level, which involves superstructures and Implants.[113]
3
Commonly when a failure occure in endodontically treated tooth, some potentially
problems for implant placement can occure due to the residual pathology. Problems like
bone resorption ora damage of bone due to infections needs bone grafting and
rexonstruction of soft-tissue.[90]
Its important to know that teeth with endodontic treatment have less complications than
implant-supported crowns, if an implant fails patient will have more negative significants
than in the case of failures in endodontically treated tooth.[96]
33
By choosing a treatment method the doctor has to keep in mind following points:
1. Restorative prognosis of the tooth
2. Physical loading characteristics
For example: in the case of a „post“ rebuild of tooth structure is needed to retain
restorations. In the case of root-filled tooth when retention is added it also increases the
risk of damaging the tooth structure.[19]
The lifetime of an implant compared to the natural tooth which is endodontically treated
and support a post and core is much higher to retain a crown.[121] Therefore, teeth which
are treated with posts have to be used in regions where they are used for example as
abutments for bridges.[32]
However there are some risks in the implant treatment such as periodontal comlications or
occlusal as well as esthetic problems. Comparing to implant-supported restorations, the
endodontic treatments have advantages such as proprioception and adaptation which are
mediated by the PDL under mechanical force.[145]
Teeth that are endoddontically treated have greater maximum bite force and efficiency of
chewing than implant-supported prostheses.[157]
The choice of the treatment to extract or retain a tooth which will affect the neighboring
teeth, especially those used as abutments is an important decision. In a study was
reported that in the case of removable partial denture which is used more than 10 years
the probability to loss the abutment is 44%.[5]
But there is not mentioned what happens to the bordering teeth when an implant is
inserted. In a big edentulous region a span of FPD is needed for extention for tooth
incorporation that need whether endodontically or peridontally therapies, which will
compromising the lifelong stability of prosthesis.[49] [10] [9] [121] [114]
34
If a tooth is decayed but not treated, it maight cause bone loss and make the dental
implantation more complex.[112] [54] [30] [88]
Placing an implant next to a tooth which is endodontically treated can be affected.
According to a suggestion of some researchers is better to prevent implantation in
positions where a tooth is clinically symptomatic (e.g. periapical pathology or radiographic
periapical pathology).Thereby its useful to extract the previously treated
neighboring tooth before implantation.[158]
However there are some researchers how have the suggestion that there is no effect on
implant prognosis if the adjacent tooth is endodontically treated
ביבליוגרפיה לדוגמא (בעבודה האקדמית כ-20 מקורות אקדמיים באנגלית ובעברית)
3. De Backer H, Van Maele G, De Moor N, Van den Berghe L Long-term results of short-span
versus long-span fixed dental prostheses: an up to 20-year retrospective study. International
Journal of Prosthodontics 21, 75–85.
34. De Backer H, Van Maele G, De Moor N, Van den Berghe L, De Boever J A 20-year
retrospective survival study of fixed partial dentures. Int. Journal of Prosthodontics 19, 143–53.
35. Doyle SL, Hodges JS, Pesun IJ, Law AS, Bowles WR Retrospective cross sectional
comparison of initial nonsurgical endodontic treatment and single-tooth implants. Journal of
Endodontics 32, 822–7.
עבודה אקדמית זו בקובץ PDF ולא הכי עדכנית ולכן בחינם. העבודות האקדמיות שברחבי המאגר שבתשלום הן בקובץ וורד פתוח ועדכניות כל זכויות היוצרים שמורות למחבר
 מאגר עבודות אקדמיות
מאגר עבודות אקדמיות 
 (לא דיינרס)
(לא דיינרס) 